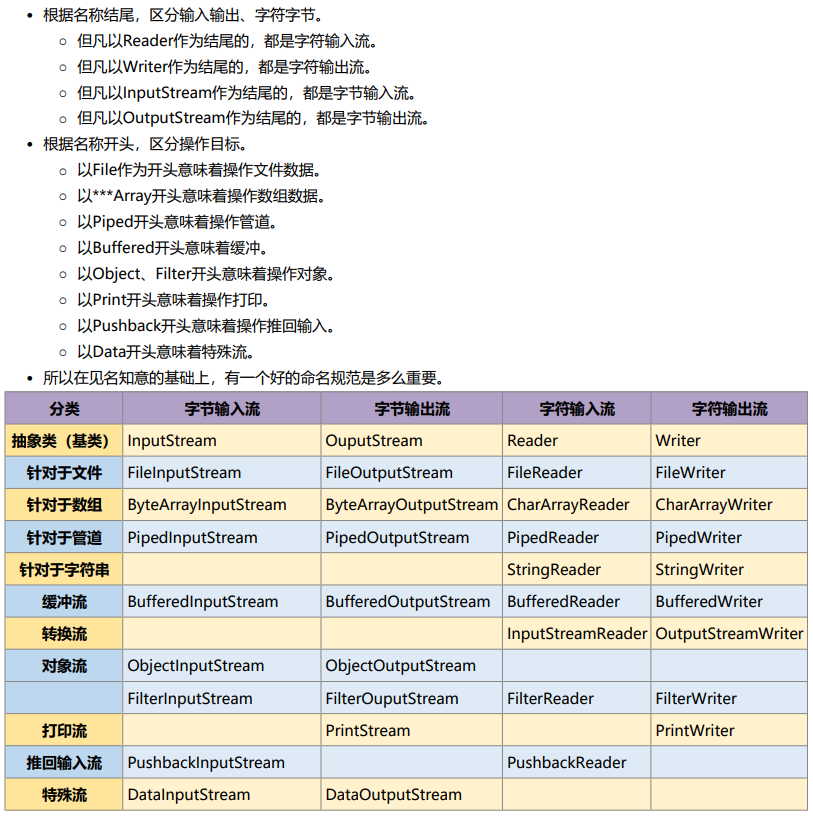
IO
FileFilter,类似于外部比较器
输入、输出、流(这是载体)
GC不会自动回收的东西:
为什么要关流?
因为JVM的垃圾回收机制不会自动回收:IO、网络、数据库等资源。
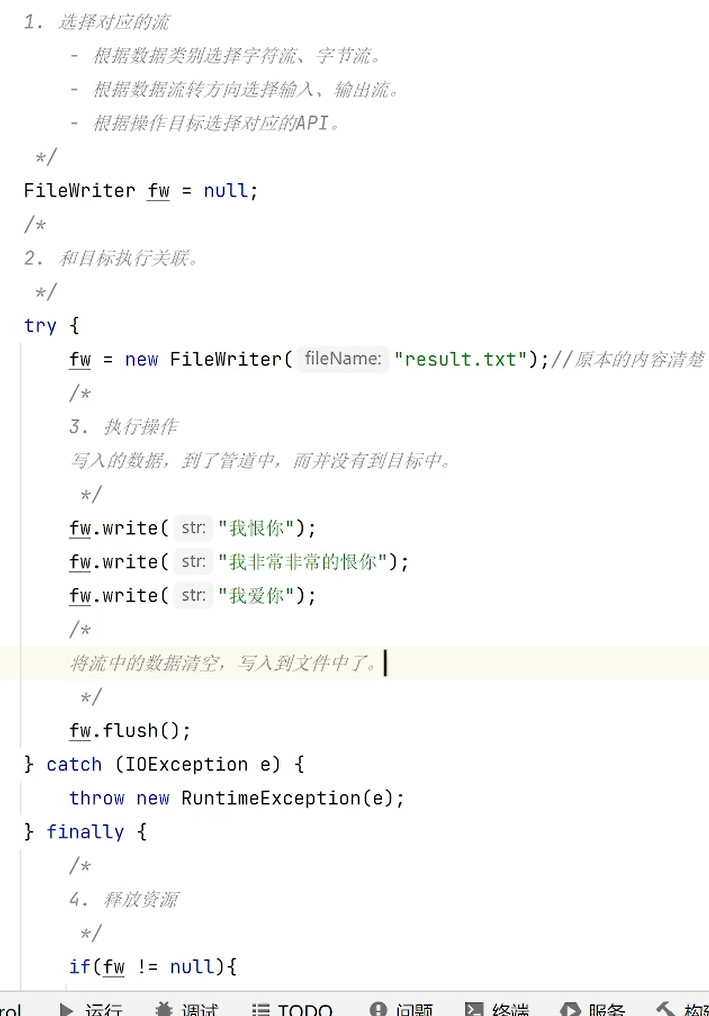
字节流
xxxReader/Writer
read()只读一个字符,返回unicode码,读不到是-1
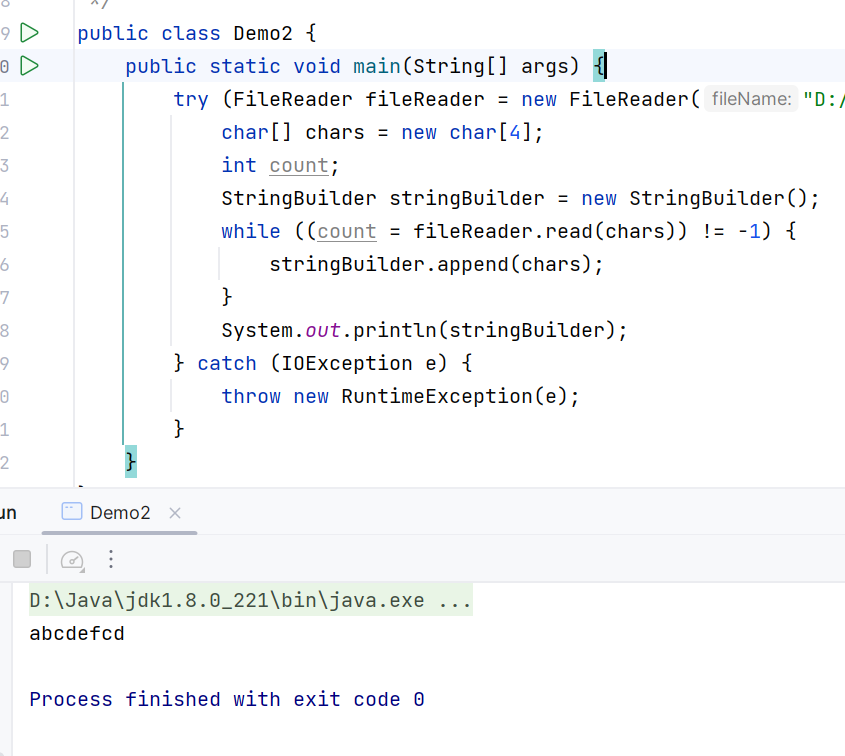
读多个字符,返回读到的数量,读不到了是-1
如果剩余字符数小于数组长度,只会覆盖前几个元素然后直接拼接(原文是abcde)
解决方案:用(chars,0,count)拼接
try-with-resource的try里面只能是实现自Autocloseable的实例化
字节流
XXXInputStream/OutputStream
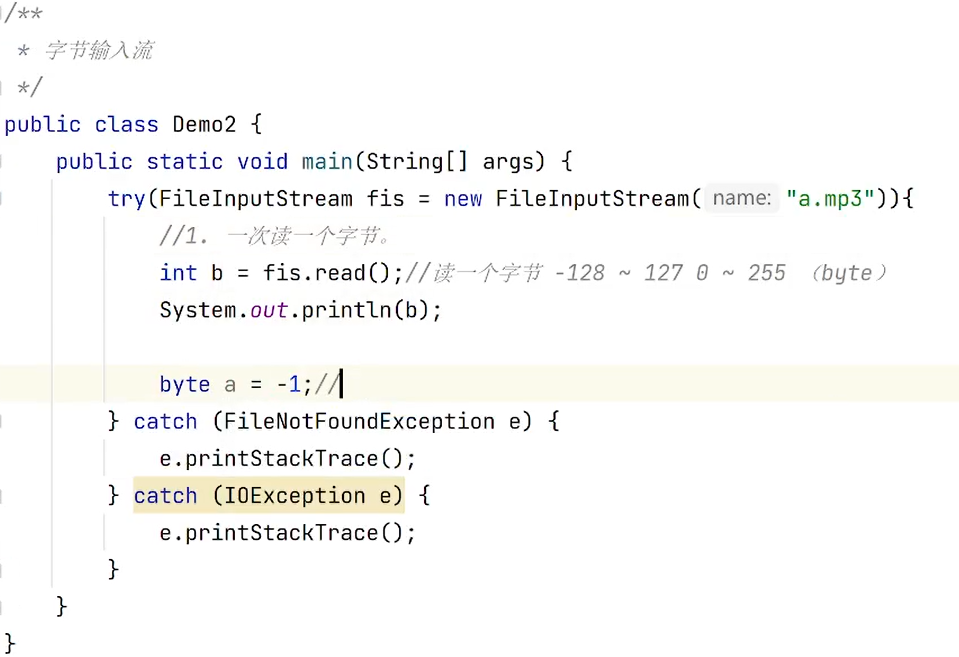
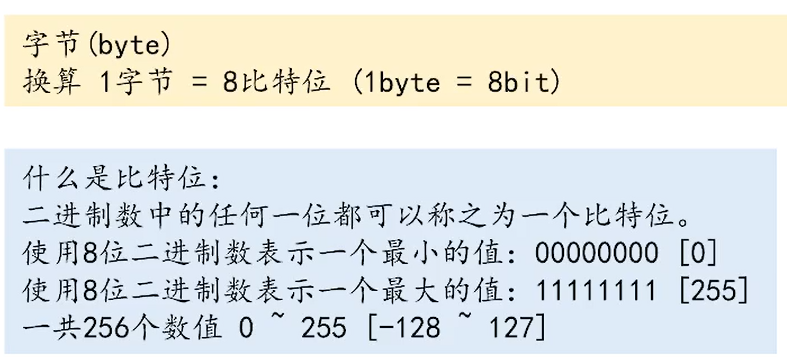
读一个字节,返回byte值(范围0~255)
读到的数量,读不到就是-1
缓冲流
- BufferedReader
- BufferedWriter
- BufferedFileInputStream
- BufferedFileOutputStream
转换流(字节–>字符)
字符流本质上也是一种字节流,可以相互转换,但是涉及到编码
| BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(""),"UTF8");
|
流的分类
按照处理数据单位划分
• 字符流:用于处理文本数据
• 字节流:用于处理二进制数据
按照方向不同划分
• 输入流:用于处理程序外部的数据输送到程序内部的操作
• 输出流:用于处理程序内部的数据输送到程序外部的操作
按照处理机制不同划分
• 节点流:程序直接和数据目标之间建立管道
• 处理流:处理流本身有很多种,是在节点流的基础上为了优化不同方面的特性而打造的一种扩展
序列化
将对象持久化到文件
序列化ID可以不用加,加了就会比对
transient序列化排除
集合ArrayList和LinkedList这种是序列化的里面的对象,不是序列化整个集合,为了节约空间
readObject,writeObject
Introduction to NIO
阻塞与非阻塞
阻塞与非阻塞是描述进程在访问某个资源时,数据是否准备就绪的的一种处理方式。当数据没有准备就绪时:
- 阻塞:线程持续等待资源中数据准备完成,直到返回响应结果。
- 非阻塞:线程直接返回结果,不会持续等待资源准备数据结束后才响应结果。
同步与异步
- 同步与异步是指访问数据的机制,同步一般指主动请求并等待IO操作完成的方式。
- 异步则指主动请求数据后便可以继续处理其它任务,随后等待IO操作完毕的通知。
烧开水:
- 普通水壶煮水,站在旁边,主动的看水开了没有?同步的阻塞
- 普通水壶煮水,去干点别的事,每过一段时间去看看水开了没有,水没开就走人。同步非阻塞
- 响水壶煮水,站在旁边,不会每过一段时间主动看水开了没有。如果水开了,水壶自动通知他。异步阻塞
- 响水壶煮水,去干点别的事,如果水开了,水壶自动通知他。异步非阻塞
模型:
参考资料
NIO
使用NIO进行文件拷贝的两种方式
FileChannel.open(Path,StandardOpenOption.XXX).read(ByteBuffer.allocate(int))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\YanXin\\Desktop\\简历投递.txt");
Path path1 = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\YanXin\\Desktop\\简历投递_copy.txt");
try (FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(path);
FileChannel fileChannel1 = FileChannel.open(path1, StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW, StandardOpenOption.APPEND)) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
int count;
while ((count = fileChannel.read(byteBuffer)) != -1) {
byteBuffer.flip();
fileChannel1.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
|
FileReader.getChannel().read(CharBuffer.allocate(int))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\IdeaProjects\\Review_JavaSe\\Module13_IOStream\\src\\result.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\IdeaProjects\\Review_JavaSe\\Module13_IOStream\\src\\result_out2.txt");
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("D:\\IdeaProjects\\Review_JavaSe\\Module13_IOStream\\src\\result.txt");
FileChannel sourceChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel targetChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
CharBuffer charBuffer = CharBuffer.allocate(3);
while (fileReader.read(charBuffer) != -1) {
charBuffer.flip();
System.out.print(charBuffer);
charBuffer.clear();
}
while (sourceChannel.read(byteBuffer) != -1) {
byteBuffer.flip();
System.out.print(new String(byteBuffer.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
targetChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
|
“BIO”, “AIO”, “NIO”
BIO:Blocking Input/Output,阻塞式IO
AIO:Asynchronous Input/Output,异步非阻塞IO,也在NIO库中(java.nio.*)
NIO:New Input/Output,No Blocking Input/Output

文件拷贝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Demo_FileCopy_Reader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\YanXin\\Desktop\\简历投递.txt"));
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\YanXin\\Desktop\\简历投递_copy.txt"))) {
String s;
while ((s = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
bufferedWriter.write(s);
bufferedWriter.newLine();
bufferedWriter.flush();
}
System.out.println("拷贝完成!");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class Demo_FileCopy_InputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\YanXin\\Desktop\\简历投递.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\YanXin\\Desktop\\简历投递_copy.txt", true)) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[6];
int count;
while ((count = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, count);
}
System.out.println("拷贝完成!");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|





